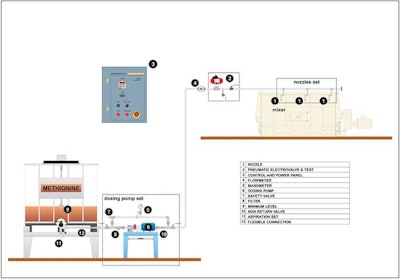
The economic, nutritional or technological attributes of liquid feed additives have made the application systems a common fixture in feed mills around the world. These liquid additives include methionine, lysine, choline chloride, organic acids and, more rarely, pigments or enzymes. This article focuses on the preventive maintenance operations, actions and verifications mill managers can perform to ensure manufacturing efficiency and feed safety.
Safety first
The main safety risks of liquid systems are directly linked to the products and their pH. Some liquid additives are classified as hazardous products and contact with the eyes or skin should be prevented.
As with powder additives, the safety data sheets of liquid additives must be accessible easily and quickly in the plant in case of any accident. Before any maintenance intervention, the plant staff or any external company should be made aware of the risks and wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as goggles, plastic gloves, covering suit, etc.
During the control visit, the presence of PPE, risks labels and spill kits will be verified. One will also check the proper functioning of the shower and eye wash stations.
Any apparent leakage of product should be fixed as soon as it is detected. The affected surfaces — pipes, pumps, floor — should be cleaned immediately. In most cases, warm water is sufficient.
Dosage accuracy
Obviously, to achieve the expected quality of the feed, each component must be added at the quantity defined by the formulator.
If the plant is using a scale for the liquid additives, its metrology will be included in the global program with the other scales for solids. It mainly consists of calibration mass verification, calibration of zero and span adjustment, if needed.
Concerning the flowmeters, the principle is to run the pump in standard working conditions and to collect the product before the mixer by a calibration valve in the bucket. The accuracy of the dosage is assessed by comparing the value measured by the flowmeter and the quantity weighed. In case of a slight deviation, parameters such as the number of pulses per liter or density must be rectified.

The control of flowmeters should be performed one to two times a year. | Adisseo
Spray quality produces homogeneity
Apart of the efficiency of the mixer and its maintenance program, it’s crucial that liquid additives are evenly applied to the solid portion of the batch.
As the viscosity of some liquids is influenced by their temperature (for example, the optimum temperature for liquid methionine is a minimum of 15 degrees C), one must ensure the integrity of the heating system and the regulation of the heating cables and pipe insulation.
The working pressure of the nozzles will influence the spray angle and the droplet size and, ultimately, the contact between the liquid and the solid phases. This pressure can be altered by the abnormal wear of the pump or by some leakages in the liquid system. Therefore, it is important to check it regularly and react in case of any deviation. In most cases, it should be between two to five bars.
The maintenance manager should take special care of the nozzles, which can run parallel to the mixer inspection and cleaning. At this point, make sure the nozzles are not blocked and that the liquid can flow freely. For specific spray patterns — for example, flatbed jet — the orientation is important and needs to be checked.
Finally, the accurate application of the liquid additive can be assessed by an annual conformity and homogeneity test, consisting of a batch produced in standard conditions and sampled. After analyzing these samples, the recovery rate (mean/expected quantity) reflects the dosage accuracy. The tolerance around the target should be between +/-10 percent and up to +/-20 percent, according to regional quality standards. The coefficient of variation (standard deviation/mean) reveals the level of homogeneity, commonly targeted to be below 10 percent.
Key takeaways
Every modern feed plant has a preventive maintenance plan, but it should also include the main verifications and actions related to its liquid additives systems. Liquid systems require light maintenance and regular inspections; however, it is important to manage the stock or the supply of the critical spare parts such as pumps, flowmeters, load cells or any electronic component. Here, failure may affect production.
In addition, every maintenance operation should be recorded, either manually or through a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
Download a liquid additive maintenance system checklist here.