Global poultry production has increasingly been influenced by consumer preferences, a push toward sustainability and new regulations which, in turn, have dictated how poultry feed is formulated. WATT Global Media’s annual Poultry Nutrition & Feed Survey offers a firsthand look at the macro trends affecting the poultry industry worldwide and provides a glimpse into the ways poultry producers, nutritionists and feed manufacturers are adapting to these changes and challenges.
The 2019 edition of the survey, conducted in late 2018, includes input from 351 respondents from around the world:
- Latin America, 39 percent
- United States/Canada, 26 percent
- Asia-Pacific, 12 percent
- Africa, 11 percent
- Europe, 9 percent
- Middle East, 3 percent
More than half of survey participants are nutritionists, consultants and veterinarians; nearly 20 percent work in live production management or as the owner of a poultry farm.
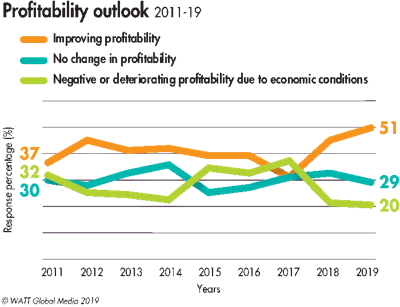
2019 profitability outlook, obstacles
Overall, survey respondents were optimistic about their company’s profitability in 2019. Fifty-one percent of respondents felt profitability will improve in 2019. While 29 percent suspect business will remain flat this year, the other 20 percent believe economic conditions will negatively impact their profits.
When asked to weigh in on the primary challenges facing their business, 79 percent cited the cost of grain and its quality (65 percent) as two of their primary concerns. Sixty-four percent of respondents feel the elimination of antibiotics due to regulation or consumer pressure is the No. 3 greatest challenge.
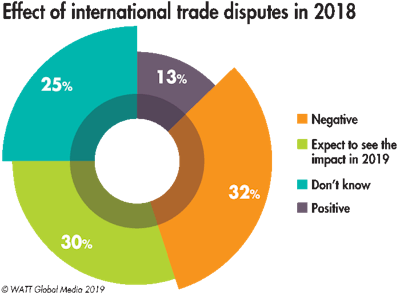
Geopolitical issues and related trade disputes in 2018 have sparked unease among survey respondents. Fifty-three percent ranked the influence of trade uncertainty as one of their top 2019 concerns. When asked how international trade disputes affected their business in 2018, 32 percent of survey participants said they experienced negative effects, and 30 percent expect to feel the ripple effect in 2019. Only 13 percent were impacted positively.
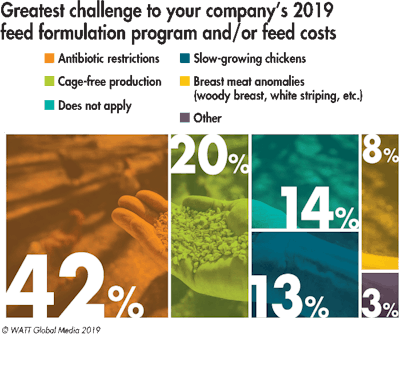
Regarding their feed cost and formulation programs, 42 percent of respondents cited antibiotic restrictions as their greatest production challenge in 2019, 20 percent said cage-free egg production and 13 percent noted slow-growing chicken production.
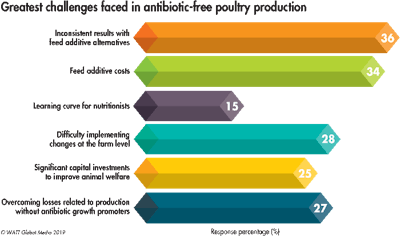
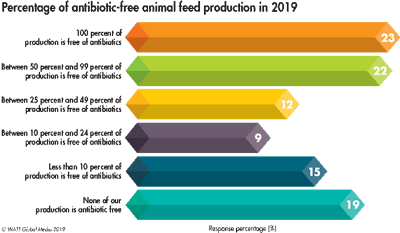
Antibiotic reduction and elimination
Eighty-one percent of 2019 survey participants report having some degree of antibiotic-free (ABF) production in their operations.
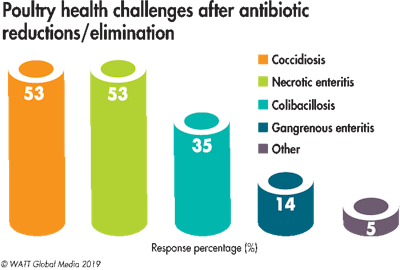
However, with these efforts, producers are experiencing additional or increased disease challenges. Since eliminating or reducing antibiotic usage in poultry feed production, respondents cite increased incidents of coccidiosis (53 percent), necrotic enteritis (53 percent) and colibacillosis (35 percent).
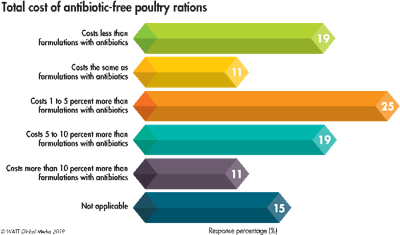
When asked to identify the total cost of antibiotic-free poultry rations, 19 percent note that their company’s formulations cost less without them; 11 percent report that their costs stayed the same. Meanwhile, 25 percent cite cost increases of 1 to 5 percent more, 19 percent say costs have increased by 5 to 10 percent and 11 percent have seen their antibiotic-free feed production costs increase by more than 10 percent.
Survey participants attribute their greatest difficulties with antibiotic-free poultry production to inconsistent results with feed additives alternatives (36 percent), the cost of feed additives (34 percent), on-farm implementation challenges (28 percent) and losses related to the elimination of antibiotic growth promoters (AGP) (27 percent).
Feed additive solutions
Sixty-seven percent of respondents report that their company is actively exploring, testing or using feed additives as antibiotic alternatives or replacements.
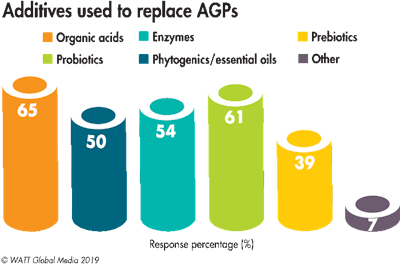
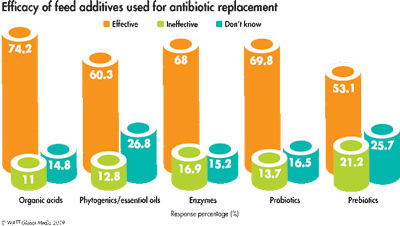
To supplement the positive production and health gains AGPs offered, survey respondents have looked to feed additives to bridge the gap. Organic acids (65 percent) and probiotics (61 percent) ranked as the most popular alternatives. Fifty-four percent use enzymes and half utilize phytogenic feed additives.
Respondents found organic acids (74 percent), probiotics (70 percent) and enzymes (68 percent) to be the most effective feed additives when seeking antibiotic alternatives. Phytogenic feed additives were deemed effective by 60 percent of respondents; however, 27 percent felt they couldn’t comment on the efficacy of the category.
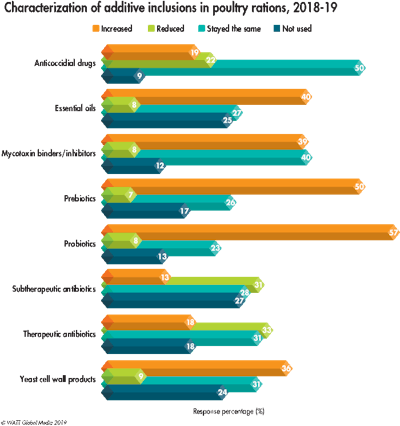
Consequently, comparing 2018 inclusions against 2019, respondents will increase their use of probiotics (50 percent), prebiotics (50 percent) and phytogenics (40 percent) this year. Thirty-two percent will decrease their use of therapeutic and subtherapeutic (31 percent) antibiotics.